Our Best Medical Programs MMBS MS/MD Nursing Dentistory PG fellowship Clinical Rotation Veterinary
Study Clinical Rotation in Abroad
Pathway program for Doctors.

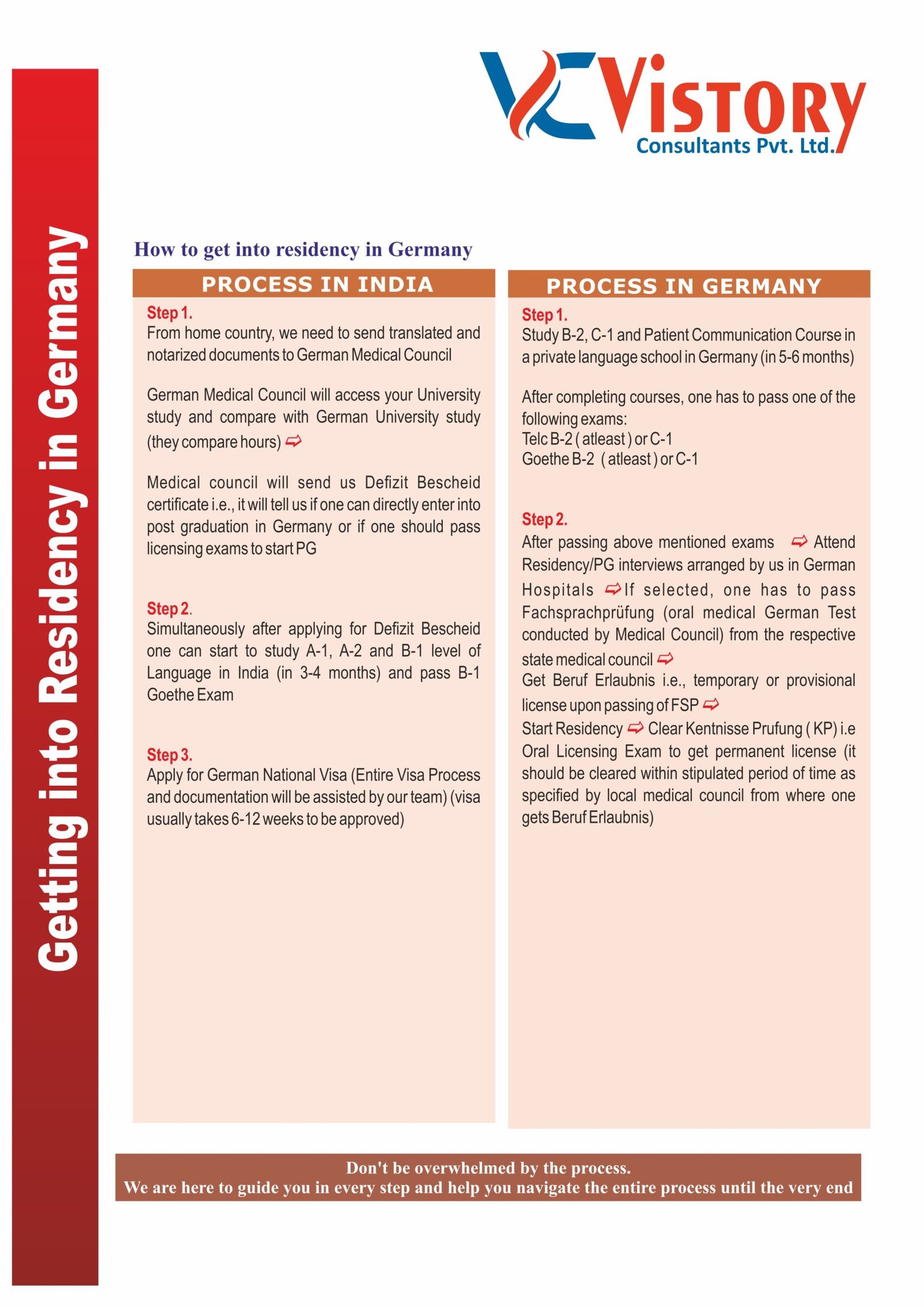


Clinical Rotation
Clinical Rotations refer to the process of medical practice where an MBBS graduate is mentored and guided by experienced professionals and practitioners as part of their medical program.
Clinical rotations serve as the culmination of a medical program, providing aspiring medical professionals with hands-on exposure to real-life scenarios in clinics and hospitals. During this phase, individuals have the opportunity to interact with actual patients, immerse themselves in the working culture of healthcare facilities, and provide treatment under the supervision of experienced physicians. By undergoing clinical rotations, individuals gain a firsthand understanding of the daily schedule and responsibilities of a licensed doctor, which prepares them for their future career.
Clinical rotations, also known as clinical clerkships, clinical training, or simply clinicals, provide an opportunity to participate in patient care and gain practical experience in diverse areas of the medical field. During these rotations, you will have a chance to apply your knowledge in real-life situations and work directly with patients.
Types of Clinical Rotation
There are several types of clinical rotations that medical students may undergo during their training:
Core Clinical Rotations: These are the essential rotations that medical students must complete, which include internal medicine, surgery, pediatrics, psychiatry, obstetrics and gynecology, and family medicine.
Elective Clinical Rotations: These rotations are optional and allow medical students to explore different areas of medicine that interest them, such as dermatology, cardiology, neurology, etc.
Sub-Internship Rotations: These are advanced clinical rotations that provide students with increased responsibility and a more independent learning experience, allowing them to function at the level of an intern.
Rural or Community Rotations: These rotations take place in a community or rural setting, where medical students have the opportunity to work with underserved populations and gain experience in a different healthcare system.
International Rotations: These rotations take place outside of the United States and provide medical students with the opportunity to learn about different cultures, healthcare systems, and medical practices.
Research Rotations: These rotations involve research projects that medical students undertake to gain experience in research methods, data analysis, and scientific writing.
Overall, the types of clinical rotations available to medical students vary depending on the medical school and program, as well as the student’s interests and career goals.
Core Clinical Rotations
Core clinical rotations are a mandatory part of medical education for all medical students. These rotations are typically completed during the third and fourth years of medical school and provide students with hands-on experience in various medical specialties.
The core clinical rotations typically include:
Internal Medicine: In this rotation, medical students work with attending physicians to diagnose and treat adult patients with a variety of medical conditions.
Surgery: Students observe and participate in surgical procedures, including pre-operative and post-operative care.
Pediatrics: In this rotation, medical students work with pediatricians to diagnose and treat children with a variety of medical conditions.
Obstetrics and Gynecology: Students learn about women’s health, pregnancy, and childbirth, and may participate in deliveries.
Psychiatry: In this rotation, students work with psychiatrists to diagnose and treat patients with mental health conditions.
Family Medicine: Students work with family physicians to diagnose and treat patients across the lifespan, including preventive care.
Completing these core clinical rotations is an essential part of medical education as they provide students with valuable hands-on experience, develop clinical skills, and prepare students for residency training.
Elective Rotations
Elective rotations refer to the clinical rotations that medical students or residents undertake to gain experience in a particular area of medicine. These rotations are typically chosen by the students or residents based on their interests, career goals, or specific skills they want to develop.
Elective rotations can take place in a variety of settings, including hospitals, clinics, and community health centers. Some common elective rotations include emergency medicine, cardiology, neurology, gastroenterology, and oncology, among others.
During an elective rotation, students or residents work closely with attending physicians, nurses, and other healthcare professionals to gain hands-on experience in patient care, diagnostic and treatment strategies, and communication with patients and their families. This experience can help them to develop their clinical skills and improve their understanding of various medical specialties.
Elective rotations are an essential component of medical education, allowing students and residents to explore different areas of medicine and gain a deeper understanding of the various specialties available to them. They also provide an opportunity for students and residents to network and build relationships with professionals in their chosen fields.










